S
Suzanne Rose
Guest
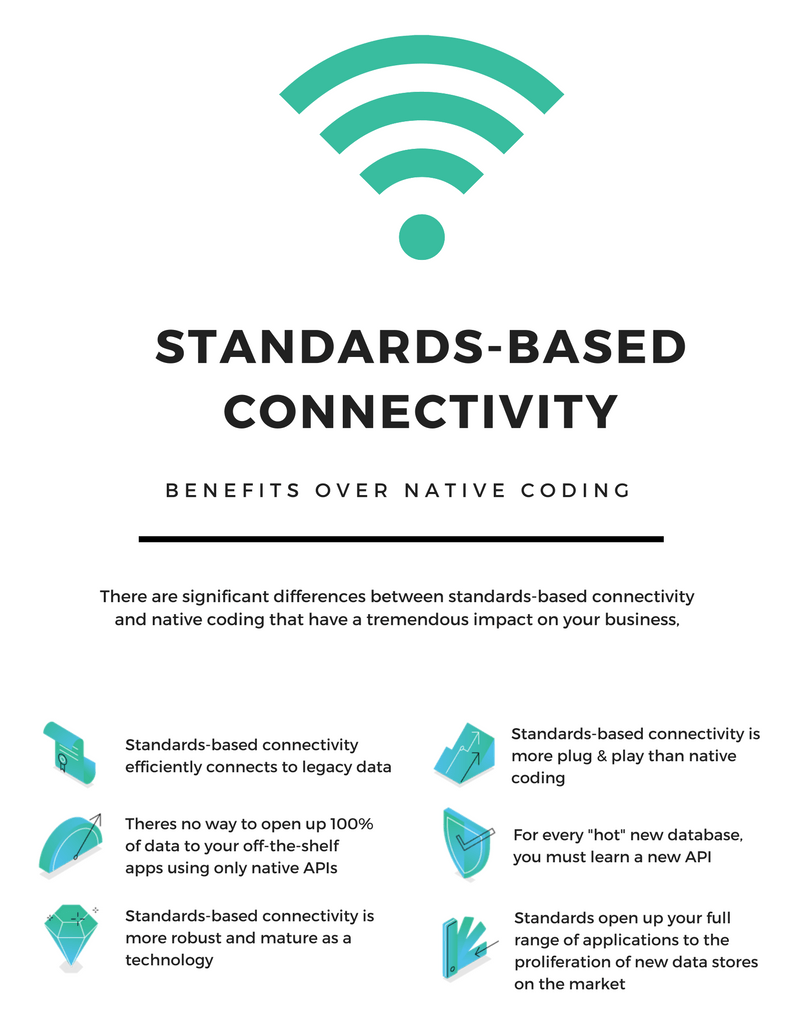
Coding native APIs is all the rage, but have you ever taken a step back and asked, “How does this compare to standards-based connectivity?” You should.
With the exponential growth of new data sources, coding to native APIs is all the rage. For example, you may want to learn to code to the Amazon Redshift API so that you can access your AWS Data Warehouse with an off-the-shelf analytics application. Or, you may have realized that Big Data and NoSQL are skyrocketing and want to learn the Cassandra API.
Whatever the case, we think you are severely limiting your scope and your choices when you choose native coding over standards-based connectivity. Here’s why:
Why Do You Need Standards?
In the Big Data ecosystem, there are two distinct, yet highly intertwined, entities: databases and applications. Applications are written in specific programming languages, and the top three most popular languages in 2016 are C, Java and Python. Databases, on the other hand, are queried via languages like SQL. Why is this important? Application and databases do not magically communicate with each other without help. A middle interface is needed to translate these languages between the application and the database in order to avoid learning and incorporating database languages inside their applications.
ODBC and JDBC were created for this exact purpose. Open Database Connectivity (ODBC), developed by the SQL Access Group in 1992, acts as a language/platform-independent translator between an application and a database. Long story short, ODBC enables your application to query and return information from any relational or non-relational database using ODBC syntax. This frees your application from needing a database-specific language. Another huge benefit is that when a database specification changes, you just need to update the ODBC driver (which we do for you very quickly).
JDBC (founded by Sun Microsystems), similar to ODBC, enables communication between the application and database as well, but in this case, using the Java programming language to talk to object-oriented databases. JDBC provides the connection between Java and databases like Oracle, Sybase and DB2. If you need to access an ODBC-compliant database using JDBC, you can do this through the use of the JDBC-to-ODBC bridge.
OData, introduced by Microsoft, is a standardized REST interface that is quickly gaining ground for its open source approach as well as its exceptional scalability. OData is referred to as “SQL for the Web” due to its ability to query across the internet. As mentioned by Mike Johnson in his post, “What Is OData and Why You Need It,” when you think about OData, you should think REST/JSON because it’s basically a standardized REST interface. This means that whenever you are able to get to a RESTful interface, you can use the OData standard. So whether you’re programming on Windows Mobile, iOS, Android or trying to use a cloud-based application such as Salesforce Connect to enrich your Salesforce data, OData can be there to help you out.
Learn More and Try DataDirect for Free
So you see the benefit of standards-based connectivity, but where do you start? It starts with high-performance, comprehensive and robust drivers. You can try any of our drivers free for 30 days. Connect any data source to any application with our enterprise-grade connectivity suite. Eight out of the top nine BI vendors partner with us for a reason.
Want to learn more about Progress DataDirect vs. Native coding? Our webinars, “SQL or SOQL for Salesforce Analytics,” and “SQL Access to Cassandra NoSQL Databases,” should give you a more technical, thorough understanding. You can view the recordings below.
SQL or SOQL for Salesforce Analytics
SQL Access to Cassandra NoSQL Databases
Get Standards-Based Connectivity Free for 30 Days
Continue reading...
With the exponential growth of new data sources, coding to native APIs is all the rage. For example, you may want to learn to code to the Amazon Redshift API so that you can access your AWS Data Warehouse with an off-the-shelf analytics application. Or, you may have realized that Big Data and NoSQL are skyrocketing and want to learn the Cassandra API.
Whatever the case, we think you are severely limiting your scope and your choices when you choose native coding over standards-based connectivity. Here’s why:

Why Do You Need Standards?
In the Big Data ecosystem, there are two distinct, yet highly intertwined, entities: databases and applications. Applications are written in specific programming languages, and the top three most popular languages in 2016 are C, Java and Python. Databases, on the other hand, are queried via languages like SQL. Why is this important? Application and databases do not magically communicate with each other without help. A middle interface is needed to translate these languages between the application and the database in order to avoid learning and incorporating database languages inside their applications.
ODBC and JDBC were created for this exact purpose. Open Database Connectivity (ODBC), developed by the SQL Access Group in 1992, acts as a language/platform-independent translator between an application and a database. Long story short, ODBC enables your application to query and return information from any relational or non-relational database using ODBC syntax. This frees your application from needing a database-specific language. Another huge benefit is that when a database specification changes, you just need to update the ODBC driver (which we do for you very quickly).
JDBC (founded by Sun Microsystems), similar to ODBC, enables communication between the application and database as well, but in this case, using the Java programming language to talk to object-oriented databases. JDBC provides the connection between Java and databases like Oracle, Sybase and DB2. If you need to access an ODBC-compliant database using JDBC, you can do this through the use of the JDBC-to-ODBC bridge.
OData, introduced by Microsoft, is a standardized REST interface that is quickly gaining ground for its open source approach as well as its exceptional scalability. OData is referred to as “SQL for the Web” due to its ability to query across the internet. As mentioned by Mike Johnson in his post, “What Is OData and Why You Need It,” when you think about OData, you should think REST/JSON because it’s basically a standardized REST interface. This means that whenever you are able to get to a RESTful interface, you can use the OData standard. So whether you’re programming on Windows Mobile, iOS, Android or trying to use a cloud-based application such as Salesforce Connect to enrich your Salesforce data, OData can be there to help you out.
Learn More and Try DataDirect for Free
So you see the benefit of standards-based connectivity, but where do you start? It starts with high-performance, comprehensive and robust drivers. You can try any of our drivers free for 30 days. Connect any data source to any application with our enterprise-grade connectivity suite. Eight out of the top nine BI vendors partner with us for a reason.
Want to learn more about Progress DataDirect vs. Native coding? Our webinars, “SQL or SOQL for Salesforce Analytics,” and “SQL Access to Cassandra NoSQL Databases,” should give you a more technical, thorough understanding. You can view the recordings below.
SQL or SOQL for Salesforce Analytics
SQL Access to Cassandra NoSQL Databases
Get Standards-Based Connectivity Free for 30 Days
Continue reading...
